Since the release of Bitcoin, the blockchain has undergone a major transformation in the media. More and more institutions, regardless of cryptocurrencies, are recognizing the benefits of the technology behind the blockchain. Even China has recently started increasingly testing blockchain technology, although all transactions with cryptocurrencies are prohibited in China. This shows how important it could become from a technological point of view. But what is a blockchain anyway and how does it work? We will go into these questions in more detail in this article.
What is a Blockchain? – Definition and Explanation
Before we go into what a blockchain is, let’s first look at the term itself. The term “blockchain” can be translated into “block chain”. What does not seem very intuitive at first glance, makes more sense when looking at the blockchain from a technical point of view. It is a kind of linked list – so quasi a chain that is extended block by block.
The blockchain with its block-by-block structure represents a decentralized database. This means that the blockchain is not maintained via a central server, but through the collaboration of many computers that can be distributed worldwide. The conditions under which a computer is involved in the blockchain depend, among other things, on the cryptocurrency itself and the underlying consensus mechanism (Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake).
The world’s largest and best-known cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, for example, relies on the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism. In this case, miners verify the transactions on the blockchain. Because the data of a transaction is stored distributed across thousands of computers, a single party cannot simply manipulate the data on the database. This would be noticed by the other participants in the blockchain.
Technically, each block in the chain contains a secure hash of the previous block. Security plays a major role anyway, so there are the following three security features for each block:
- Hash (security of the previous block)
- Start and confirm transaction
- Timestamp
The blockchain is therefore a kind of decentralized, non-manipulable booking system in which a large number of parties can participate. There is no central authority that rules over the blockchain. The decentralized database managed by multiple participants is referred to as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
How Does a Blockchain Work?
Now that we have clarified what a blockchain is, we want to examine in more detail how the blockchain works. The blockchain is a complex construct that is not easy for laypeople to understand.
Important: Transactions on the blockchain build on each other. This means that they are always based on previous transactions. This ensures that a new transaction cannot be falsified. This proves that the transaction is in its rightful place. Since a new transaction is always based on the last one, the transaction history cannot be falsified. Incidentally, not only cryptocurrencies benefit from the functionality of blockchain technology, but the decentralized networks are also used in other areas and, according to experts, are likely to conquer the markets in the coming years, in various industries.
The following infographic illustrates how it works.
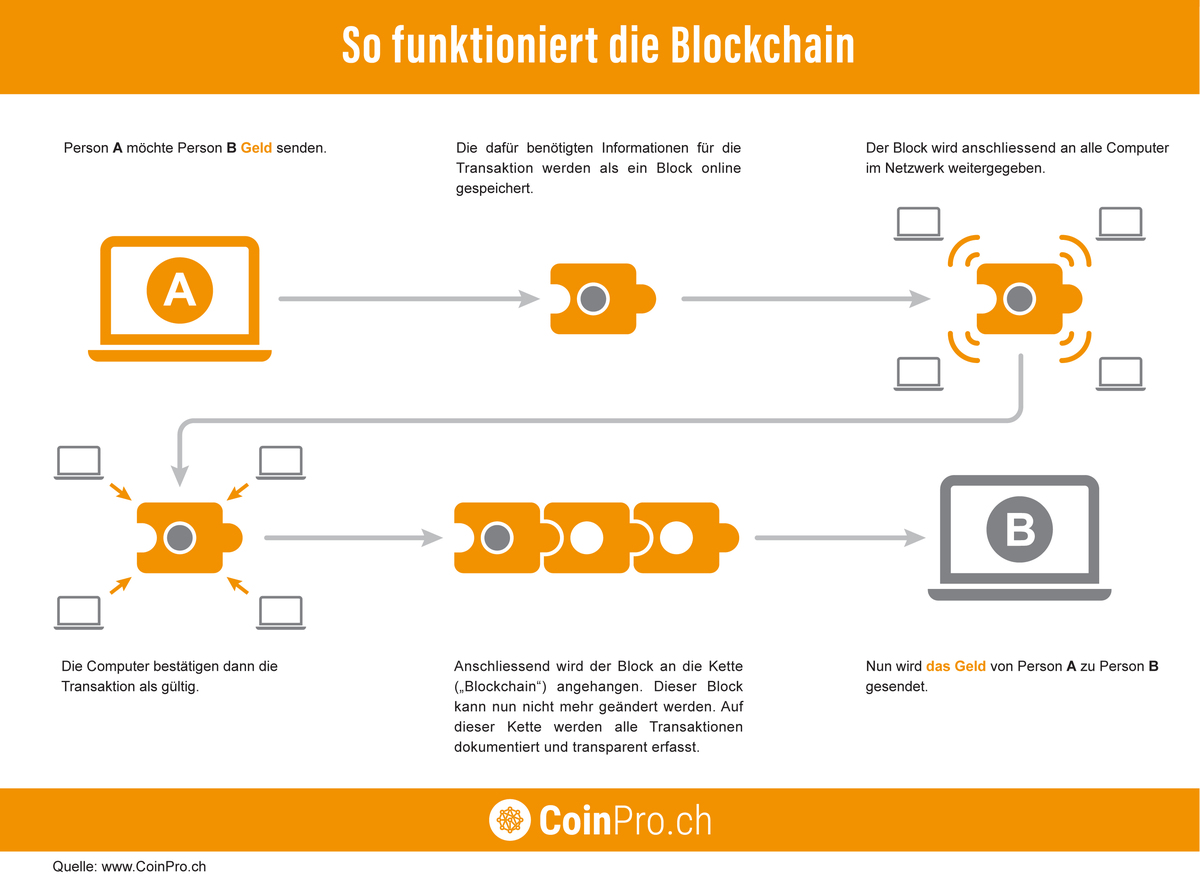
- In the initial situation, person A wants to send money in the form of digital currencies to person B.
- For this purpose, all important information of the transaction is digitally stored in a so-called block.
- The block is then forwarded to all parties (computers) connected to the network.
- In the next step, these parties confirm the transaction as valid.
- After that, the block of the said transaction is attached to the existing chain. This makes the transaction irrevocably and transparently stored and visible to all participants in the network.
- And finally the money is sent from person A to person B.
The Functionality in the Video
under CC BY-SA 4.0 license: SRF/Einstein/Christian Bachmann
How is a Blockchain Structured?
If you trade with cryptocurrencies or want to pay with Bitcoin, for example, it is of course not absolutely necessary that you understand the technology behind it and are familiar with the blockchain. However, some people also deal with Mining, i.e. mining new coins, and then at least basic knowledge is definitely an advantage. Therefore, in the following we would like to give a brief overview of how the blockchain is structured:
- Data records become data blocks
- Data blocks contain multiple transactions (including checksum)
- Hashing takes place within a block
- Data blocks become the blockchain
- Production of new blocks through mining
Since the blockchain is designed in such a way that one block is attached directly to the next block, the database as such can continue to grow steadily and is not limited in principle (except for the technical possibilities themselves).
The Advantages and Disadvantages
We now want to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of blockchain technology. The advantages are obvious. Since no central authority has control over the blockchain, the blockchain represents a public database that anyone can view. The following graphic highlights the advantages of the blockchain:
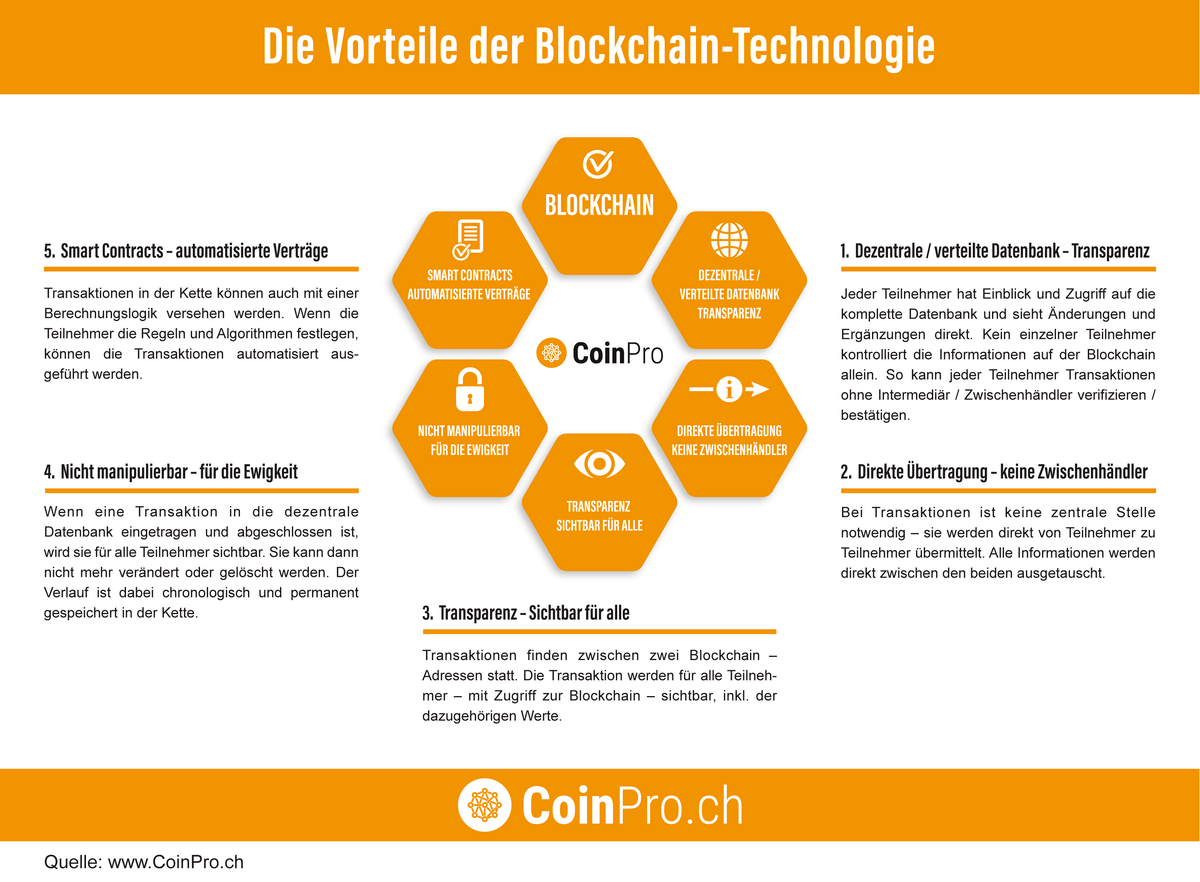
The blockchain essentially offers five areas where it can solve or improve current problems.
- Decentralized / distributed database – Transparency: Every participant has insight and access to the complete database and sees changes and additions directly. No single participant controls the information on the blockchain alone. This allows each participant to verify / confirm transactions without an intermediary.

1. Decentralized / distributed database – Transparency - Direct transmission – no intermediaries: No central authority is necessary for transactions – they are transmitted directly from participant to participant. All information is exchanged directly between the two.
- Transparency – Visible to all: Transactions take place between two blockchain addresses. The transactions are visible to all participants – with access to the blockchain – including the associated values.
- Non-manipulable – for eternity: When a transaction is entered into the decentralized database and completed, it becomes visible to all participants. It can then no longer be changed or deleted. The history is chronologically and permanently stored in the chain.
- Smart Contracts – automated contracts: Transactions in the chain can also be provided with a calculation logic. If the participants define the rules and algorithms, the transactions can be executed automatically.
Of course, the blockchain also carries some risks. In particular, the so-called 51 percent attack regularly comes to the fore. This is an attack on a blockchain by applying more than half of the computing power. This could allow one party to. The larger the network, the less likely such an attack is. Therefore, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are very secure. Other cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum Classic (ETC) have already fallen victim to such an attack.
Conclusion: What You should Know about the Blockchain
As a decentralized database, the blockchain offers the possibility to execute transactions easily and securely. In contrast to centralized databases, it is not necessary for there to be a controlling authority.
This makes it possible to automate many processes that previously had to be monitored additionally. You don’t have to worry about the data being manipulated, provided it is a secure blockchain. The more participants the network has, the more secure it usually is. However, there are differences between Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work blockchains. You can invest in them by trading cryptocurrencies or by investing in shares of companies that rely on the blockchain.


