Ethereum has been in second place behind Bitcoin for several years. Many observers consider the project to be the most promising cryptocurrency of all. Why is that? Coinpro takes a look at the special features and capabilities of ETH.
Trade Bitvavo now at Bitvavo:
European exchange with EU license (MiCA)
over 180 cryptocurrencies
10 Euro sign-up bonus
- Deposit via PayPal
- Staking available
- low fees
Ethereum Explained: the Basics
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum is not just a digital means of payment, but also a so-called smart contract platform. The option of executing scripts without an intermediary is intended to give users even more self-determination and freedom.
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum (ETH) is the world’s first user-operated networkBlockchain that provides smart contract functionality. The so-called “smart contracts” can execute scripts based on the blockchain. In this way, ETH established decentralized finance (DeFi). The symbol of the project is Ξ.
In addition to a blockchain, there is a cryptocurrency of the same name, which is often shortened to Ether. It serves as a native means of payment within the ecosystem. All transactions must be paid with Ether, even if NFTs or ERC-20 tokens are sent via the blockchain.
NFTs, ERC-20 tokens and similar standards are also based on smart contracts. Independent developers can use it to create their own currency based on ETH or issue certificates that serve as proof of ownership.
Although NFTs have so far mainly been used as a gimmick, as proof of ownership they can even be linked to physical assets such as real estate. This could eliminate the need for intermediaries such as notaries. The role of the state is also decreasing.
Many users see the wide range of capabilities as an indication that Ethereum will one day be the largest cryptocurrency of all.
Who Invented Ethereum?
The inventor of Ethereum is Vitalik Buterin. The programmer, who was born in Russia, conceived ETH as early as 2013. He then looked for supporters with whom he began working on the project.
Together with Charles Hoskinson, Gavin Wood, Anthony Di Iorio, Mihai Alisie, Amir Chetrit, Joseph Lubin and Jeffrey Wilcke, Buterin founded Ethereum in the spring of 2014. Some of the people involved are still active in other crypto projects today and are among the crypto celebrities. The first publication of the blockchain took place on July 30, 2015.
What is Ether (ETH)?
Ether is a synonym for the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain. The term can be used to indicate linguistically that the term in question is not the blockchain, but its currency.
Ether can serve as a P2P means of payment just like Bitcoin. However, it develops its greatest importance through dApps and tokens, which are used as partially dependent projects via Ethereum.
If a user wants to make a transaction via Ethereum, they must always have Ether to pay the network fees that the nodes receive for providing the network. They are also called Gas Fees in the Ethereum network.
This rule also applies if he wants to send a token other than the native currency, such as an NFT or a stablecoin. The sending of such a token cannot be paid for with the token itself.
Ether is also the largest unit of account of the cryptocurrency. This can be divided into the smaller parts Wei, Kwei, Mwei, Gwei, Twei and Pwei. In reality, these units usually have no meaning. Usually, a small amount of ETH is simply specified with decimal places in Ethereum itself. The namesake for the unusual units of account is the Chinese programmer Wei Dai.
How Does Ethereum Work? – Possible Ethereum Use Cases
Ethereum’s functions are what make the crypto project special, but what exactly can the blockchain achieve through its smart contracts? We take a look at specific use cases and find out why ETH managed to establish the most popular sector in the crypto industry.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and Gas
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is usually encountered in its abbreviated form – EVM. The EVM is the programming level of Ethereum. It processes all smart contracts and accounts of the blockchain. The Ethereum Foundation formulates its meaning as follows:
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is the environment in which all Ethereum accounts and smart contracts live.
When processing data, ETH distinguishes between two different account types. On the one hand, there is the external account (EOA) and on the other hand, the contract account.
Both account types have the same basic functions. They can receive, send and hold Ethereum and ETH tokens. In addition, they can interact with smart contracts.
An EOA is used by all normal users. It can be created free of charge and has the option of initiating payments. Coins and tokens can only be received without creating a new smart contract. The user who has power over the private key has control over an EOA.
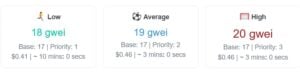
Within the Ethereum network, users pay gas fees when they commission transactions. In other blockchain networks, similar fees are simply called network fees. Users pay these fees to the validators of the network, who are responsible for processing the transactions. The price of gas fees is denominated in Gwei. One Gwei is one millionth of an ether.
Smart Contracts and the Ethereum Blockchain
A contract account costs money and, unlike the EOA, is therefore not free. Depending on the type and functions, the price per contract account varies between several tens of thousands of Gwei. The costs are incurred because the program code stored in the contract takes up storage space that the network must provide.
Such a contract account contains the smart contracts for which ETH is essentially known. Thanks to these scripts, processes can run automatically and avoid an intermediary, for example when providing loans.
The buyer must, of course, pay the price of the contract account in the native currency of the blockchain – ETH. Other currencies such as stablecoins or fiat currencies cannot be used for this.
A smart contract cannot initiate an initial money transfer. A transaction is only possible once a payment has been received. A contract account contains smart contracts that can be triggered by deposits.
When the program code is started, a token is paid out, for example, or a new smart contract is created, which then in turn follows new, predefined conditions.
Contract accounts are not under the control of a person with a private key. There is no private key for a contract account. Instead, it follows the logic of smart contracts. This makes it possible to use these scripts as a decentralized platform for applications.
What are Ethereum dApps?
Smart contracts then form the backbone of so-called dApps. The word dApp stands for decentralized application. Unlike today’s mostly common centralized applications, a central instance does not have the decision-making power over the processes in a dApp.
Instead, these processes are processed automatically by smart contracts. This methodology is intended to ensure neutrality towards users. The aim is to prevent censorship. Well-known dApps on Ethereum are the DEX Uniswap, the stablecoin marketplace Curve Finance or the NFT trading platform OpenSea.
DApps resist the injustice that arises from centralized apps. There, the responsible companies (e.g. Facebook, Google or other Big Tech companies) have absolute power and can do as they please. DApps are intended to bring more freedom to the individual user.
Many crypto enthusiasts hope that Web3 will be able to replace the current Web2 in the future. Web3 is the latest version of the Internet and is based on decentralized applications instead of centralized apps.
What Can Ethereum be Used for? – Possible Use Cases
Ethereum, just like Bitcoin, can be used as a censorship-resistant, free currency. However, the focus of the crypto project is on its function as a DeFi blockchain – i.e. as a platform for smart contracts. Ether serves as a means of payment there. Actions on the blockchain must be paid with it.
Independent developers can develop their own applications, which then live on ETH and therefore function as decentrally as the blockchain itself. There are no limits to the imagination.
So far, financial applications are particularly popular. However, social networks such as Facebook, Instagram or Twitter are also conceivable on the basis of Ethereum. This idea has already been implemented with the Lens Protocol.
Growing interest in NFTs can be assumed in the future. These are digital ownership certificates that have so far mainly been used in digital worlds or for digital works of art. However, they can also appear as proof of ownership for a physical object such as a house or a plot of land.
What are Ethereum ICOs?
Ethereum itself carried out an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) in the summer of 2014. The developers of the cryptocurrency sold 60,102,215.232 ETH to investors for a price of 31 US cents per coin. In total, the Ethereum Foundation and the founding community were able to secure a financial injection of 16 million US dollars.
A few months later – in 2017 – the so-called ICO Boom developed. Independent developers created their own tokens, which Ethereum’s ERC-20 standard had made easier than ever before.
They equipped these mostly pointless tokens with the wildest promises. In some cases, they expanded their marketing with advertising campaigns. Many of the projects generated millions through the ICOs – the crypto exchange Gemini puts the damage at a total of ten billion US dollars.
This ICO boom, also known as Ethereum ICOs, primarily produced scams that damaged the public image of pre-sales. Gullible investors therefore acquired tokens that had no use. Most of those responsible intentionally did not keep the promise of building a benefit in the future.
The Ethereum ICOs were the responsibility of third parties. The developers of Ethereum themselves did not participate in this. The name is due to the fact that Ethereum served as the basis, as most of the cryptocurrencies offered were based on the ERC-20 standard.
Ethereum Staking & Mining
For a long time, Ethereum relied on the proof-of-work method, similar to Bitcoin. New Ether coins were mined in an energy-intensive process. With Ethereum Mining you could strengthen the Ethereum network and receive new Ether coins as a reward. In the meantime, Ethereum has switched to the proof-of-stake consensus algorithm as part of many updates. This means that Ethereum Mining is no longer possible.
Instead, new blocks are created through a so-called proof of stake, we will now call the process itself Ethereum Staking. Owners of Ether Coins can act as validators from a balance of 32 ETH and thus secure the network. In order to be able to participate in staking as an average Ethereum owner, you can therefore also stake Ethereum via crypto exchanges or so-called liquid staking providers.
All details about Ethereum Staking
What is ETH 2.0?
Ethereum is working on a huge upgrade, at the end of which Ethereum is to become Ethereum 2.0 (also ETH 2.0). Its previously low scalability of 10 to 15 TPS (transactions per second) is to increase to as much as 100,000 TPS.
At the same time, energy efficiency is to increase and the need for powerful computers for mining is to disappear. All these measures are being carried out in order to achieve mass adoption of Ethereum.
Proof of Stake and the resulting staking play a crucial role in this development. In order to achieve the high throughput of 100,000 transactions per second, Ethereum wants to process the majority of money transfers via partially dependent blockchains, which are called Shard Chains.
Proof of Stake is beneficial to ensure the security of these subchains. In this way, a large number of shard chains can be easily secured through staking. If ETH were to use Proof of Work for this, each of these blockchains would need its own network of miners. The effort for this would be enormous.
In the course of the development of Ethereum 2.0, a new concept was also developed, which the programmers call Danksharding. With this system, the various shard chains do not create their own blocks, but data blobs.
Just like a normal block, these blobs contain transactions. The special feature of Danksharding is that shard chains do not each maintain their own blockchain, but forward the blobs to a central Block Proposer (block creator). This central instance then decides which transactions are included in the next block.
In this way, Ethereum wants to force a departure from MEV. In simple terms: The developers want to prevent monetary interests from leading to rising network fees or even censorship.
The shard chains or sub chains are intended to fulfill the role of a Layer-2 Rollups. The previous Ethereum mainnet now bears the name Beacon Chain. This Beacon Chain serves as a consensus level on which all transactions continue to be summarized.
The Future of Ethereum: Forecast for the further ETH Course
Ethereum is considered one of the crypto projects with the greatest potential. More and more users believe that ETH will one day even overtake the eternally first-placed Bitcoin – this hypothetical event is called Flippening.
However, shortcomings in scaling meant that Ethereum lost more and more market share in the DeFi sector over a long period of time. The currently second largest cryptocurrency itself founded this. Today, the DeFi sector is the most competitive sector within the crypto industry.
In December 2022, in addition to ETH, there are seven other projects in the top 20 cryptocurrencies that provide smart contract functionality. Many of these projects are only a few years old. Since they are considered to have a particularly promising future, they have achieved a rapid rise.
The implementation of Ethereum 2.0 is crucial for Ethereum to be able to prevail against this major competition. You can read what development CoinPro predicts for the next few years in our Ethereum price forecast.
How Can I Buy Ethereum?
Ethereum, just like any other cryptocurrency, can be purchased via crypto exchanges. For most users, the most convenient trading platform is a centralized crypto exchange such as Bitvavo, Bitpanda or Binance.
In the guide, where can you buy Ethereum, CoinPro provides a detailed guide for buying the digital investment. In short, the creation and identification of an account is necessary. Swiss francs or another fiat currency can then be deposited using conventional methods such as a bank transfer or card payment.
Users can then use this fiat money to purchase the cryptocurrency of their choice. Since Ether is the second-largest cryptocurrency, the investment can be purchased on almost any crypto marketplace.
Users who value their personal privacy more can use P2P exchanges to purchase ETH without identification and without an intermediary. Platforms such as Paxful or Localcryptos are suitable for this. The fees are higher here.
Ether can also be purchased with another cryptocurrency via a DEX. Cross-chain swaps like THORChain even make this option possible across blockchains.
Trade Bitvavo now at Bitvavo:
European exchange with EU license (MiCA)
over 180 cryptocurrencies
10 Euro sign-up bonus
- Deposit via PayPal
- Staking available
- low fees



